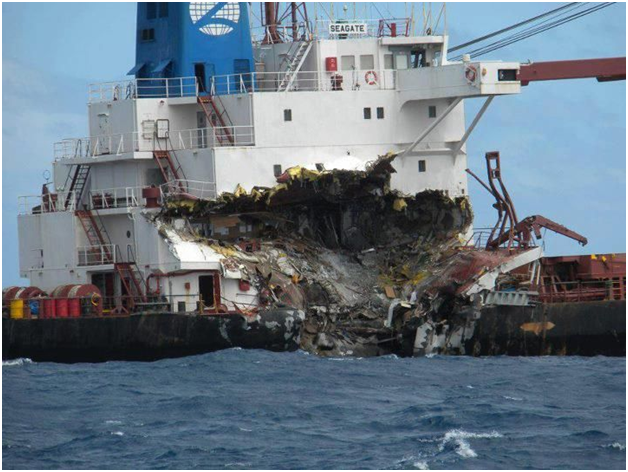
Q. How does Indian Administration conducts inquiries and investigations into shipboard casualties on foreign ships visiting its ports.
a. Elaborate with the mention of relevant international codes and relevant sections of the MS ACT 1958.
b. Define Marine Casualty
c. What does the Marine Safety Investigation report consists of and how is it relayed to the IMO by member state responsible for conducting this investigation.
d. What are the procedures for conducting an inquiry after casualty at sea as per merchant shipping act 1958, as amended? What is Article of agreement? Why is it necessary to have an Article of agreement?
Answer:-
a) Definition of shipping casualty
- For the purpose of an investigation and inquiry, a shipping casualty shall be deemed to have occurred in the following cases:
- Any ship is lost, abandoned, stranded or materially damaged on the coasts of India
- Any ship causes loss or material damage to any other ship on the coast of India
- Any loss of life occurs due to any casualty happening to or onboard any ship on the coasts of India
- Any evidence of an Indian ship being lost at sea is available in India
Master’s action
- On his or his ship’s arrival in India, master shall report the incident to the officer appointed by the central government
- If the ship is materially damaged to make her un-seaworthy or any loss of life or serious injury occurs, then the owner or master should report to nearest principal officer within 24 hours
Investigating officers
The following officers have been appointed by the central government for receiving reports and conducting investigations into the shipping casualties
1. Principal officer /MMD surveyor – all casualties
2. Deputy conservator of major port – when casualty within the docks or if the ship belongs to the port or where pilot is on board
3. Port officer of minor port – any casualty involving sailing vessels and fishing vessels or involving ships with in port jurisdiction
4. Customs collector – sailing vessels and fishing vessels
5. Officers specially appointed – fire and explosion casualties
Investigating officer’s action
- Inform central govt. that a casualty has occurred
- Conduct and preliminary enquiry(PI)
- Record the statement of master’s, crew members with their signature, but without presence of any person
- Call for documents from the ship as appropriate
Send report to central govt. with one or more of the following recommendations
a) No further action
b) Warning to defaulters
c) Strict warning to defaulters
d) Issue M.S. notice
e) Order formal investigation (FI) or court. of inquiry(CI)
- PI report is totally confidential and not given to any court
- Copies of statement are given to the affected persons only if matter goes to the court
- The officer at his own discretion or as advised by central government may apply to first class or metropolitan magistrate for conducting a formal inquiry.
Circumstances for ordering FI or CI
- Heavy material loss requiring more detailed investigation
- Defaulters deserve to be punished (only court can order that)
- There are lessons to be learnt from the casualty
- Public out cry
- Loss of life, so open court investigation is required
- Sufficient data not collected during PI
- During the FI if a case of incompetence, misconduct wrongful act arises against master, mate or engineer, court will proceed with the CI
If central government believes that there are grounds for charging the officer as stated above without conducting a FI, then it may submit a case to the court for conducting a CI. This will apply only if the officer holds—
- An Indian certificate
- A foreign certificate but was employed on an Indian ship
Procedure for FI and CI
- A short statement of case with a questionnaire to be answered at the end of FI and CI are submitted to the court
- If central government has decided to directly proceed with the CI, then in addition to the above documents, a charge sheet framed against the defaulters is also submitted
- The proceeding are conducted in an open court
- The court can summon/compel the attendance of a witness, by arresting him if necessary
- For FI, court shall appoint 2 to 4 assessors chosen from a list prepared by central government, one of them shall be conversant with maritime affairs and the other with maritime or mercantile affairs
- If FI involves cancellation or suspension of certificate of an officer, two of them shall have the experience in merchant service
- All documents collected during the PI are submitted
- On completion of FI or CI the report is published in the official gazette
b) Article of agreement
- This agreement is made between employer/agent and seafarers in accordance with collective bargaining agreement
- Details of employees seafarers ( address, next to kin, passport details, CDC details etc will be furnished in that
- Details of employment including monthly wages, monthly PF, monthly allotment, rank, reason for sign off etc will be mentioned
- This contains signature with date and stamp of employee
- Signature of seafarer (signed on ashore, ship, signed off ship, ashore)
- Signature with date and stamp of master (signed on ship, signed off ship)
- Signature with date, stamp of shipping master[on commencing employment concluding employment ]
Terms and conditions
1. This agreement between employer and the seafarers is subjected to the condition that seafarers will serve in capacity/rank on wages indicated with other terms on employment as CBA
2. This agreement shall be serving in the area and for the period as agreed as CBA
3. The seafarer will be supplied with provisions not less than what is provide in the M.S.act /CBM which is higher
4. It is agreed that the rights, duties and the terms of employment of seafarers and the obligations of the ship owner as per ILO conventions ratified by India