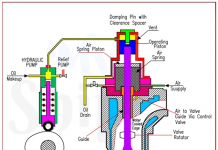
Human Resource Management(HRM) is the term used to explain official framework devised for the management of people within an organization. These human resources responsibilities are normally categorized into 3 major areas of management: staffing, employee compensation, & defining or designing work. Generally, the purpose of HRM is to increase the productivity of an organization by optimizing the efficacy of its employees. This directive is unlikely to change in any fundamental way, despite the ever increasing pace of change in the business world. Edward L. Gubman noticed in the Journal of Business Strategy, “the basic mission of human resources will be to acquire, develop, & retain talent; position the workforce with the business; & be an excellent backer to the business. Those three challenges will never change.”
PRINCIPLES OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Business consultants note that modern human resource management is directed by several dominant principles. Possibly the paramount principle is a simple identification that human resources are the most significant property of an organization; a business can’t be successful without efficiently managing this resource. Another essential principle, formulated by the Michael Armstrong in his book A Handbook of the Human Resource Management, is that business success “is most likely to be achieved if the personnel policies & procedures of the enterprise are closely linked with, & make a major endowment to, the achievement of corporate targets & tactical plans.” A third guiding principle, same in nature, holds that it is HR’s accountability to find, secure, guide, & develop employees whose talents & preference are suited with the operating needs & future goals of the company.
POSITION AND STRUCTURE OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Human resource management department function can be classified by individual, organizational, & career areas. Individual management require helping employees recognize their strengths & weaknesses; rectify their shortcomings; & make their best support to the enterprise. These duties are carried out through a different activities such as performance reviews, training, & testing. Organizational development, aim on promoting a successful system that maximizes human & resources as part of larger business plans. This imminent duty also covers the creation & continuation of the change program, which enable the organization to act to advance outside & internal influences. The 3rd duty, career development, necessitate matching individuals with the most appropriate jobs & career paths within the organization.
Human resource management responsibility are ideally placed near the theoretic center of the organization, with permit to all areas of the business. HRM department is responsible for influencing the productivity & development of workers at all levels, human resource personnel must have access to—and the support of—key decision makers. In addition, the HRM department should be associated in such a way that it is able to practically communicate with all areas of the company.
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT—KEY RESPONSIBILITIES
Human resource management is associated with the progress of both individuals & the organization in which they work. HRM, is involved not only in securing & developing the ability of individual workers, but also in executing programs that improve communication & cooperation between those individual workers to nurture organizational development.
The main function related with the human resource management covers: job analysis & staffing, organization & utilization of work force, measurement & appraisal of work force performance, implementation of reward systems for the employees, professional development of workers, & maintenance of work force.
Job analysis consists of finding with the help of other company areas the nature & duties of various employment positions. This can include confirmation of the skills & experiences required to adequately work in a position, recognition of job & industry needs, & prediction of future employment levels & skill requirements. “Job analysis is the foundation of the HRM practice because it gives correct information about jobs that is utilized to hire & promote people, fix wages, find training needs, & make other important HRM decisions. Once the recruiting part has been over, selection is done through job postings, interviews, reference checks, testing, & other tools.
Organization, utilization, & maintenance of the company work force is another main work of the HRM. This covers forming an organizational procedures that makes utmost use of the enterprise human resources & establishing systems of communication that help the organization work in a unified manner. Other duties in this area covers safety & health & worker management relations.
Performance appraisal is the practice of evaluating employee job performance & providing feedback to those employees about both positive & negative side of their performance. Performance measurements are very essential both for the organization & the individual, for they are the primary data used in deciding salary increases, promotions, &, in the case of workers who work unsatisfactorily, dismissal.
Reward systems are generally commanded by the HR areas as well. This feature of the human resource management is very important, for it is the system by which organizations give their workers with rewards for past achievements & incentives for better performance in the future. It is also the system by which organizations address problems within their work force, through institution of disciplinary procedures.
Employee development & training is another crucial duty of the HR people. HR is accountable for review an organization’s training needs, & for commencing & assessing employee development programs planned to address those needs. These training programs differs from the orientation programs, which are planned to acclimate the new employees to the company, to the aspiring education programs formulated to acquaint workers with a new software system. After obtaining the suitable talent into the company, the second conventional task to the human resources is to line up the workforce with the business—to continuously build the capacity of the workforce to perform the business plan.” This is achieved by performance appraisals, training, & other activities. In the arena of performance appraisal, HRM personnel should develop uniform appraisal standards, develop review techniques, instruct managers to manage the appraisals, & then assess & follow up on the success of performance reviews. They should also tie the appraisal process into compensation & incentive strategies, & work to assure that federal regulations are followed.
THE CHANGING FIELD OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
In contemporary years, some business tendency have had a remarkable effect on the broad field of HRM, principal among them were the new technologies. These new technologies, generally in the areas of electronic communication & information spreading & retrieval, have dramatically changed the business landscape. Satellite communications, computers & networking systems, fax machines, & other gadget have all enable change in the ways in which businesses interrelate with each other & their workers. Telecommuting, for example, has become a very favoured option for many workers, & HRM professionals have had to form new guidelines for this prominent subset of employees.
Basics Relationships between employees and management are of substantial value in any workplace. Human relationship is the procedure of training employees, conveying their needs, promoting a workplace culture & solving dispute between different employees or between employees & management. Understanding some of the the method that human relations can effect the costs, competitiveness & long-term economic sustainability of the business helps to underscore their significance.
Human relations in the office are the main part of what makes the business work. Employees should frequently work together on the projects, communicate ideas & impart motivation to get things done. Without a stable & inviting office culture, unfavourable challenges can appear both in the logistics of controlling employees & in the bottom line. Businesses with attractive offices & the well-trained employees are more likely to retain & attract qualified employees, promote loyalty with customers & more quickly adjust to meet the needs of the changing marketplace.
Improving Retention
The quality of office relations is interpretative to the employee retention. Employee retention may seem insignificant mainly in the office that is used to a high turnover, but managers should keep in mind that turnover is financially very costly. Every new employee needs a considerable investment of time & energy in their recruitment & training. Severing ties with the old employees can sometimes be demanding, mainly if the condition are not particularly cordial. Making sure quality employees remain interested & engaged in the business requires patience, compassion & flexibility, but can generally make the business more financially sound.
Motivation and Productivity
Office relationships come up with a source of employee inspiration, which is significant in maintaining productivity. Employees those are interested in their work & in the success of other employees tend to be more productive than those who are not. This productivity pays obvious financial benefit to the company, as it can get more done in less time with fewer costs. Building relationships, by both recognizing an employee’s value to the company & a responsibility for their needs, often goes a long way.
Fostering Creativity
The contemporary business environment often benefit businesses that are able to swiftly invent products that meet changing client needs. In some industries such a technology, e.g. — employees capacity to come up with productive new ideas is often the difference between the entire company’s success & failure. According to Sallyport Magazine, research shows that creativity is based to large degree in social interaction. Employees’ creativity is often dependent on their ability to communicate with other employees and share ideas. Without quality workplace relationships, employees are less likely to be able to develop and share the solutions that a business needs to survive.