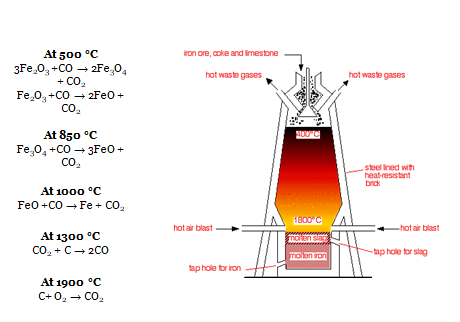
- Ore is heated in furnace with Coke to a temperature of 1800 °C
- Various reactions at different stages in furnace
- C + O2 = CO2 ( at bottom)
- CO2 + C = 2CO
- Fe2O3(s) + 3C(s) → 2Fe(l) + 3CO(g)
- This Fe produced is in molten state is passed through sand bed to produce Pig Iron.
The function of the limestone
Iron ore is a mixture of rocky material that would not melt at the temperature of the furnace, and would eventually clog it up. The limestone is added to convert the mixture into slag which melts and runs to the bottom. The heat of furnace decomposes the limestone to give calcium oxide.
CaCO3→CaO+CO2
This is an endothermic reaction, absorbing heat from the furnace. Hence it is important not to add too much limestone because it would otherwise cool the furnace. Calcium oxide is a basic in nature and reacts with acidic oxides such as silicon dioxide present in the rock. Calcium oxide reacts with silicon dioxide to produce calcium silicate.
CaO+SiO2→CaSiO3
The calcium silicate melts and flow down through the furnace to form a layer on top of the molten iron. It can be tapped off from time to time as slag. Slag is used in road making and as “slag cement” – a final ground slag which can be used in cement, often mixed with Portland cement.
Processes to remove impurities from pig iron.
- Open hearth process—pass CO
- Bessemer process– pass Air
- L & D process– cooled oxygen at 11 bar.
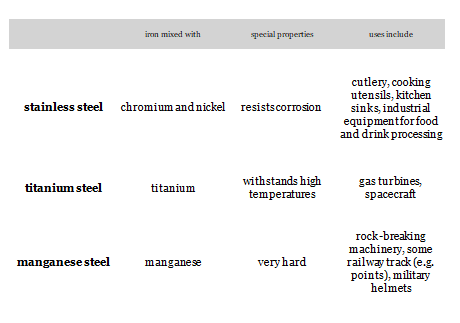
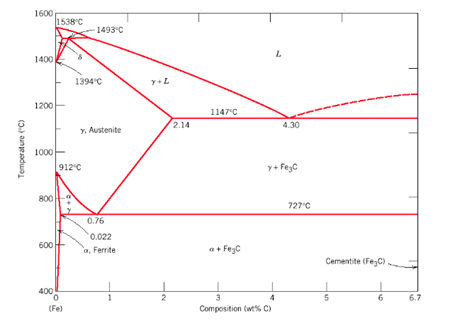
- Low carbon steel ( Mild Steel)– 0.05% – 0.3%
- Medium carbon steel — 0.3% – 0.5%
- High Carbon Steel — 0.5% – 1.8%
- Cast iron– 1.8% – 4.2%
- Cementite – 4.2% – 6.63%