What is I.S.M. ?
The International Management Code for the Safe Operation of the Ships and for Pollution Prevention (International Safety Management (ISM) Code).
What is I.M.O. Convention ?
Conventions are main instruments of IMO, being binding legal instruments, regulating some aspect of maritime affairs of major concern to IMO e.g. SOLAS & MARPOL.
They are recognized by name and the year of adoption by the Assembly, Such as the International Convention on the Safety of Life at Sea, 1974.
May have comprehensive technical provisions attached in annexes, such as 6 annexes to the MARPOL convention, each dealing with a different aspect of marine pollution.
How many conventions are there ?
About 50 ? Though checked up to 1998, 25.
What is a Protocol ?
A treaty instrument which makes major changes to a Convention which has been adopted but not yet in force. The Protocol usually speeds up the Convention’s entry into force. e.g. MARPOL 73/78, SOLAS 74/78
Name some major IMO Conventions ?
ON MARITIME SAFETY:-
- International Convention on the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), 1960 and 1974.
- International Convention on Load Lines (LL) 1966.
- Special Trade Passenger Ship Agreement (STP) 1971.
- International Regulations for Preventing Collision at Sea (COLREGS), 1972.
- International Convention for Safe Containers (CSC) 1972.
- Convention on International Maritime Satellite Organization (INMARSAT), 1976.
- Torremolinos Protocol of 1993 relating to the Torremolinos International Convention for the Safety of Fishing Vessels (SVP-F), 1995.
- International Convention on the Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping of Seafarers (STCW) 1978.
- International Convention on Maritime Search and Rescue (SAR), 1979 and
- International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping, for Fishing Vessel Personnel (STCW-F) 1995.
- STCW 1978 was revised at a conference in London which is held in July 1995, the revised convention is generally known as STCW-95.
MARINE POLLUTION CONVENTIONS:-
- International Convention Relating to Intervention on the High Seas in Cases of Oil Pollution Casualties (INTERVENTION) 1969.
- Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matters (LC) 1972.
- International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, 1973, as modified by the Protocol of 1978, relating thereto (MARPOL 73/78) and
- International Convention on Oil Pollution Preparedness, Response and Co-operation (OPRC) 1990.
LIABILITY AND COMPENSATION CONVENTIONS:-
- International Convention on Civil Liabilities for Oil Pollution Damage (CLC), 1969.
- Convention relating to Civil Liabilities in the Field of Maritime Carrriage of Nuclear Materials (NUCLEAR) 1971.
- International Convention on the Establishment of an International Fund for Compensation for Oil Pollution Damage (FUND) 1971.
- Athens Convention relating to Carriage of Passenger and their Luggage by Sea (PAL) 1974.
- Convention on Limitation of Liability for Maritime Claims (LLMC) 1976 and
- International Convention on Liability and Compensation for Damages in Connection with the Carriage of Hazardous and Noxious Substances (HNS) 1996
CONVENTIONS CONCERNING OTHER SUBJECTS:
- Convention on Facilitating of International Maritime Traffic (FAL) 1965.
- International Convention on Tonnage Measurement of Ships (TONNAGE) 1969.
- Convention for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts Against the Safety of Maritime Navigation (SUA) 1988.
- Protocol for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts Against Fixed Platforms Located on the Continental Shelf (SUAPROT) 1988 and
- International Convention on Salvage (SALVAGE) 1989
How many conventions have been ratified by Bangladesh?
Bangladesh has ratified 13 conventions including those on SOLAS, Loadline, Tonnage, STCW 78/95, COLREG, STP, INMARSAT, FAL.
What is SOLAS & MARPOL ? How many annexes are there in MARPOL ?
SOLAS stands for International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea.
MARPOL stands for International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships.
There are at present 6 annexes to MARPOL :-
- Prevention of Pollution by Oil
- Prevention of Pollution by Noxious Liquid Substances carried in bulk
- Prevention of Pollution by Harmful Substances in Packaged Form
- Prevention of Pollution by Sewage
- Prevention of Pollution by Garbage
- Prevention of Air Pollution (NOX nitric oxide, SOX- sulphur oxide)
How many chapters are there in SOLAS ? Which chapter contain ISM & which one with safety of bulk carrier ?
There are 12 chapters in SOLAS. Chapter 9 deals with the ISM and Chapter 12 with bulk carrier safety.
What are enhanced surveys and which type of ships are required to have them ?
Normally these are detailed inspection of the welded joints of ship’s side shell frames in selected holds, and extensive thickness measurement, carried out by IACS member societies on (1) dry bulk carriers and (2) tankers.
Continuous survey of bulk carrrier and tankers are being phased out and Enhanced survey program has been extended from 4 to 5 years with an Intermediate survey between Special surveys. Special survey program for the Tankers, more than 10 years of age.
What are harmonized system of survey and certification (HSSC) ?
All SOLAS, MARPOL and Loadline Convention Certificate including certificates issued under the International gas (IGC) and chemical tanker (BC) codes and BCH Code for older tankers can be done at one go. Therefore the ship will no longer have to go out of service for survey to meet the requirement of one convention shortly after having to do so for another convention. It means that all certificates for cargo ships will have a 5-year maximum validity (previously Cargo Ship Safety Equipment Certificate have a validity for a maximum of 2 years, while cargo ship Safety Radio Certificate was valid for only one year), however Passenger Ship SEC will be valid for one year only. It came into International effect on 3/2/2000.
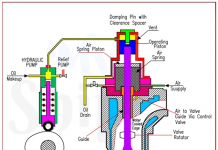
What is DOC, SMC, DPA, NC in ISM
DOC– Document of Compliance
SMC-Safety Management Certificate
DPA is Designated Person Ashore
NC– Non-conformity
When will be the ISM Code be fully implemented ?
It is in force for bulk carriers, passenger ships and tankers. It will come into force for all other ship types on 1/7/2002.
What are the objectives of ISM Code ?
The objectives are to ensure safety at sea, prevention of human injury or loss of life and damage to the environment and to property.
What is non-conformity ?
A situation in which objective evidence indicates the non-fulfillment of a specified requirement.
Who issues DOC and SMC ?
Flag state administration(FSA) or authorized classification societies on their behalf
What is Tonnage and Load line Convention ?
Tonnage Convention deals with the internationally acceptable system of measurement of ships volume in order to set dues on the vessel.
Load line Convention deals with the minimum required freeboard measurement and watertight integrity of the vessel.
What is STCW ?
STCW is Standard of Training, Certification and Watch keeping.
What are the objectives of STCW?
The objectives of the STCW is to set the minimum level of competence among seafarers internationally.
What is ‘ppm’ ?
‘ppm’ is parts per million.
Discharge criteria for the ships other than oil tankers and for machinery space of oil tankers wef 6/7/1998:-
- The ship must be proceeding on a voyage
- The ship must not be within a special area
- The oil content of the affluent does not exceed 15 ppm
- The ship must have in operation equipment required by regulation 14
Discharge criteria within a special area:
- In Antarctic Special Area, total prohibition
- The bilge water must not originate from cargo pump room bilges
- The bilge water is not mixed with the cargo residue
- The ship is proceeding on voyage
- The oil content without dilution does not exceed 15 ppm(Parts Per Million)
- The ship has in operation an oil filtering system complying with Regulation 16(5)
- The filtration system is equipped with an automatic stopping device when effluent level
What is the rule for discharge of (a)E/R bilge and (b) pump room and slop tanks ?
(1) For E/R bilge refer to above answer
(2) For pump room & slop tanks, all the following condition must be satisfied.
- The tanker is proceeding on a voyage,
- The tanker is not within the marpol annex-1 special area,
- The tanker is not less than 50 nautical miles from the nearest land,
- The instantaneous rate of discharge of bilge does not exceed 30 litres/nautical mile
- For tankers which entered into their service in before or since 1980, total quantity discharged does not exceed 1/15000 of the total quantity of cargo and tankers which entered into service after 1980, 1/30000 of the total quantity of particular cargo.
What is SOPEP and IOPP ?
SOPEP is Shipboard Oil Pollution emergency plan.
IOPP is International Oil Pollution Prevention certificate.
What is standard and International Shore Connection ?
Standard connections are used for discharge of bilge, sludge, sewage or electrical connection.
International shore connection is for connecting with the fire main for water supply from sources other than ship’s main and is located as per Safety/Fire plan.
If there is any accidental discharge during bunkering, what is your action ?
- Stop bunkering operation
- Contain pollution and prevent overboard spillage.
- Inform port authorities.
- Follow SOPEP.
What are the entries in ORB Part-1 ?
(1) Any movement of E/R oil,
(2) Bunkering,
(3)Date and time of operation,
(4)Incineration,
(5) Discharge through the approved equipment for E/R bilges and
(6) To shore reception facilities (sludge).
What is Cargo Record Book ?
Cargo Record Book refers to the chemical tankers and entries must be made in relation to each tank affected by the following operations:
- Loading of cargo
- Internal transfer of cargo
- Unloading of cargo
- Cleaning of cargo tanks
- Ballasting of cargo tanks
- Discharge of ballast from cargo tanks
- Disposal of residues from cargo tanks
- Disposal of residues to reception facilities
- Disposal of residues into the sea as per schedule to the regulation
- Removal of residues by ventilation
- Emergency/accidental discharge
- Records must be retained for three years from the date of last entry.
What is IMDG Code ?
IMDG Code is the acronym of International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code. This document explain about the various classes, packing, marking and segregation of dangerous goods and marine pollutants carried in packaged form. MFAG (Medical First Aid Guide) and EmS (Emergency Schedules) are the supplement to the IMDG Code.
What is WHO and ILO ?
WHO is acronym of World Health Organization, ILO is acronym of International Labor Organization.
Name one of the major ILO Convention for seaman ?
ILO 147 which is also called the Minimum Standards Convention. This Convention requires ratifying states to have:-
- Regulations laying down for the ships registered in their territory,
- Safety standards, including the standard of competency, hours of work and manning,
- Appropriate social security measures and
- Shipboard conditions of employment and living arrangements.
What is class notation, tonnage marks, load line and Plimsoll mark ?
The ship’s character of classification symbols (e.g. +100A) is known as class notation. Here the “+”(Positive) sign means the ship was constructed under survey by classification society surveyors, ‘A’ means the ship was constructed or accepted into classification class and is maintained in a good and efficient condition. Additional notation like ‘IWS’ for in-water survey etc.
Tonnage marks are inscribed on the hull indicating the gross and net tonnage as per ITC-69.
Plimsoll and load line marks refer to impressions on the outer hull to indicate the depth or draft up to which the vessel may be loaded before proceeding to sea in salt water and are calculated on the basis of Load Line Convention 1966.
What is flag administration and what is its roles ?
Flag administration is the national bureau for registration of ships. Its duty is to implement various national and international legislation to which the flag state is a party. In Bangladesh it is the Department of Shipping.
What are classification societies and under whose authorities do they work?
Classification societies are bodies that decides standards for the construction and maintenance of ships. Compliance with standards which are published as Rules of the particular classification society ensures assignment and maintenance of class.Classification societies act under the authority delegated to them by the flag administration.
How many national shipping regulations we have got till now ?
There are five regulations:
- Iso-76 (inland shipping ordnance 1976)
- Mso-83 (merchant shipping ordnance 1983)
- Flag vessel protection ordnance 1982
- Maritime zone act (setting out limits of territorial water, contiguous zone and eez)
- Light house act
Which chapter of SOLAS deals with Bulk carrier safety?
Chapter -12
What are the legal basis of Survey?
What stands for the following- MARPOL, SOLAS, STCW?
How many chapter are in SOLAS ? ISM is which chapter?
What are the certificates to be retained on board as per SOLAS ?
Which certificates to be retained on board?
Bangladesh ratified how many conventions?
Bangladesh shipping act + ordinance- how many?
What is mean by Maritime zone act? What is EEZ ?
ISO ’76 deals with ? MSO deals with ? Maritime zone act ?
ORDINANCE:-
decree – president pass a law without parliament
act – through parliament
rule – from the act(subdivision from act passed by ministry of law)
convention – multilateral treaty in a forum
Routine associated with handing over, taking over and accepting a watch:
Handing over a watch:
- Main & Auxiliary machineries, boiler, A/C, refrigeration, steering, electrical motors, alternators etc. They are working in good order or any changes from normal, abnormality to be informed.
- Stand by machinery are at Standby mode and emergency equipments are at ready mode.
- Status of communication with bridge to inform.
- Any fresh orders or instruction from Chief Engineer Officer
- Any repairs/maintenance in progress
- Any pending jobs which are undergoing e.g. Ballast or any other critical operations.
- Environmental protection in good order e.g. Smoke etc is in acceptable level.
- M/E rpm/ ship speed status
- Safety related items e.g. Fire alarms on duty/in order, bilge level etc. Informed good condition
- Any other information regarding maneuvering in congested water navigation, bad weather precaution as appropriate.
- Log Book updated on time, all parameters logged down, meter readings recorded as appropriate
- For UMS ship alarm record book and equipment check lists to be verified
- Call the relieving engineer officer in time and handover the duty, if you are satisfied that the relieving engineer officer is in fit/good condition; not drunk etc. If in doubt inform the chief engineer officer
Taking over a watch
- Reach the engine room(ER) on time, take a good round to feel for any abnormality in sound, smell etc.; check for any leak, contamination, level, pressures and temperatures.
- All above items mentioned for handing over to be covered or checked
- Log book and observed parameters to be in matching condition.
- For the UMS ship alarm record book and equipment check lists to be verified
- If in doubt inform chief engineer officer
Accepting Watch
If all above check points are covered satisfactorily, watch is taken over smoothly. If in doubt – may consult chief engineer
- Collection of machinery space log book & understanding significance of readings taken
- In general while taking over or handing over a watch, considering a smooth running operation, all parameters – pressure, temperature, level, flow meter reading etc. are normal and logged down in the log book correctly. Should there will be any abnormality following significant difference will appear:
- Change in temperature and pressure will indicate deviation or abnormality, considering same ambient condition
- Difference in level condition indicates loss, leakage, overflow etc.
- A distillate plant flow meter small reading may indicate performance fall off.
- Fuel oil or diesel oil flow meter increased reading may indicate loss of above, leakage etc.
- In short any changes in engine room(ER) log book parameters will help to make out difference between condition monitoring and easily detects some fault with relevant machineries and indicate their performance
Routine duties undertaken during a watch:
Q: How will you ensure duties undertaken performed in good order?
a) Take regular rounds to ensure complied
b) Also check for any bad smell, abnormal sound, and look for any abnormality, leakage, level etc.
c) Actually a good watch keeping helps keep aware of any changes and decision can be made out accordingly.
d) Bridge or chief engineers any instruction should be completed with
e) Any incomplete repairs, bilge, ballast operations to be supervised carefully.
f) During the congested water navigation, bad weather, appropriate decision should be taken. For any type of issue with main & auxiliary machines, bridge or chief engineer officer to be informed as appropriate, meanwhile preventive or corrective action to be taken
Safety precautions to be done during a watch and immediate actions in the event of a fire or accident:
Q: What precautions to be followed during a watch?
- Regular rounds to observe for bad smell, abnormal sound or noise,leakage,level etc.
- Main, auxiliary machinery, steering gear etc. Pressure & temperature, level to be maintained normal, main engine RPM, vessel speed normal
- Boiler, pressure, level, Air conditioning, refrigeration, pumps etc in order
- Exhaust or smoke checked clear, bilge level, normal, fire duties, active
- No excessive bilge level, ballast, transfer operation taking place.
- Take corrective actions to change in parameters and inform chief engineer or bridge when appropriate.