Dual-fuel merchant ships are vessels equipped to run on two different types of fuel, typically a combination of traditional marine fuel (diesel or HFO) or cleaner alternatives such as LNG (liquefied natural gas) or methanol. The flexibility of dual-fuel engines allows ship operators to switch between fuels depending on availability, cost, and environmental regulations.

SOURCE: MARINELINK.COM
- The operational procedure of a dual-fuel engine is quite simple.
- The engine works on diesel fuel as well as it also operates on natural gas by injecting it to the combustion chamber.
- The dual-fuel engine has a control system that regulates the amount of natural gas that is injected into the combustion chamber.
- The control system controls the amount of natural gas injection to maintain the engine’s efficiency. The natural gas is ignited by diesel fuel, providing the necessary heat to ignite the gas.
- The dual-fuel engine operates best at moderate or high load conditions.
SOURCE: MARITIME-PROFESSIONALS.COM
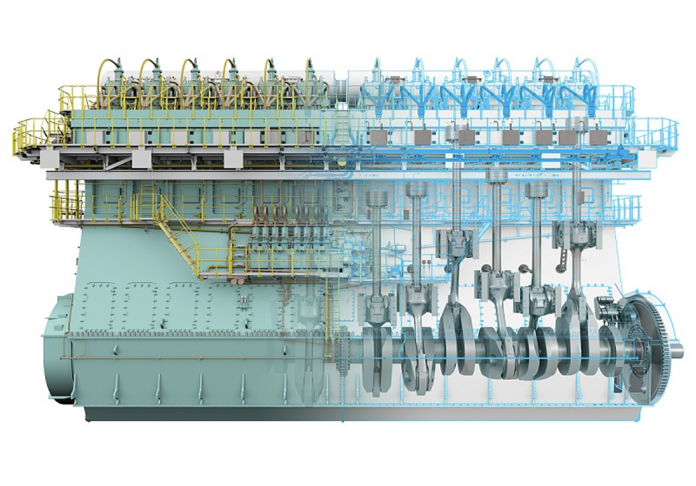
WORLDS MOST POWERFUL DUAL-FUEL ENGINE WinGD 12X92DF
There are several types of dual fuel engines including the diesel pilot ignition engine, the spark ignited engine (S.I.), MAN 51/60 DF, the ME-GI (M-type electronically controlled gas injection) engine and the WARTSILA 2-STROKE X-DF engine.
SOURCE: MARITIMEPROFESSIONAL.COM
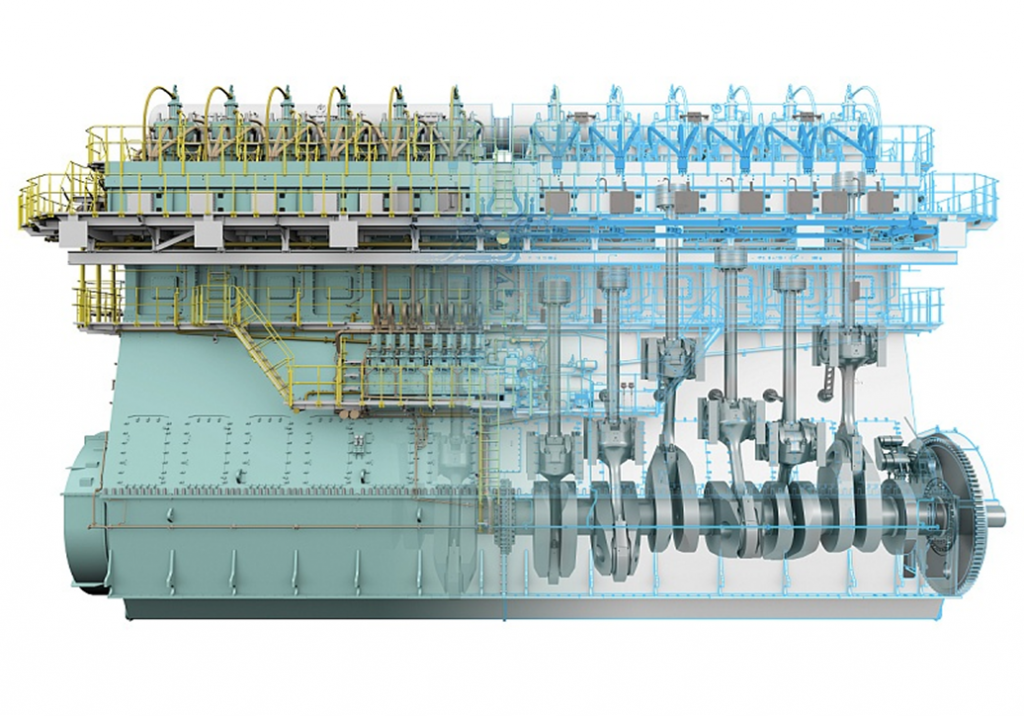
- The most common type of dual-fuel engine is the diesel pilot ignition.
- The DPI uses diesel fuel as the pilot fuel and natural gas as the main fuel.
- The ME-GI is a newer type of dual-fuel engine that uses a high-pressure gas injection system. It operates on the principle of micro-pilot ignition, where a small amount of diesel fuel is injected into the combustion chamber to ignite the natural gas.
- Also, the SI engine uses natural gas as the main fuel and diesel fuel as the pilot fuel. The natural gas is ignited by a spark plug which eliminates the need for diesel pilot fuel.

SOURCE: FLEETSHIP.COM
WHAT IS RETROFITTING?
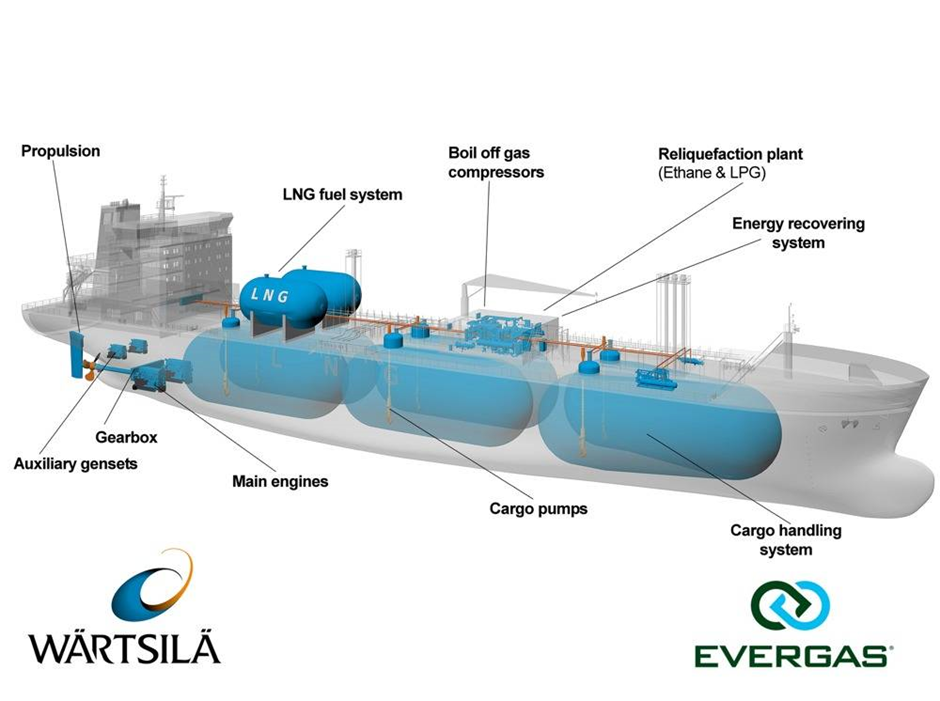
Retrofitting is the process of modifying the existing marine engine to run on dual fuel or on cleaner fuel alternatives or to run on a second sustainable fuel. The conventional fuel will primarily be traditional one like HFO or diesel one, the sustainable one will LNG, or methanol or biofuels etc.
Though, retrofitting is a very costly process which involves making changes or replacement of fuel storage tanks and fuel supply system and that range between 5-15 million USD depending on the type of fuel. Also, the retrofitting involves a single fuel engine to dual fuel engine is a very complex process and which involves and requires significant expertise.
SOURCE: GLOBAL MARITIME FORUM.ORG
WHY USE OF LNG OR METHANOL?
- LNG and methanol are both cleaner fuels or alternatives to traditional fuel such as HFO, VLSFO etc. LNG is a cleaner, non-toxic, colourless that is formed by cooling natural gas to -162 degree Celsius whereas methanol is a colourless flammable liquid that formed from natural gas or biogas.
- Methanol has a lower carbon footprint than LNG with blue methanol have 5-10% less CO2 than LNG. Methanol is easier to store, handle and cheaper than LNG.
- Although, LNG has higher density than methanol hence, energy provided per unit volume is more in LNG than methanol.
- Also, life of LNG has longer shelf life than methanol which can be important for long voyages.
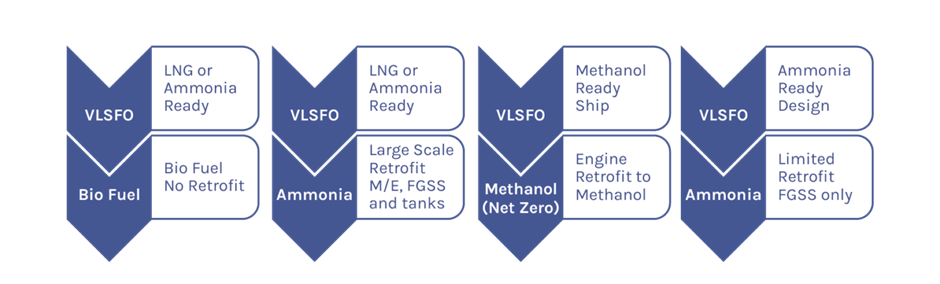
SOURCE: GLOBAL MARITIME FORUM.ORG
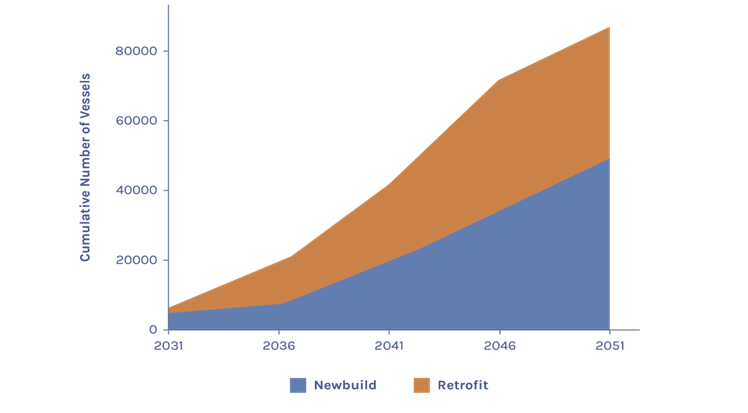
SOME POTENTIAL PATHWAYS FOR RETROFITTING
Here are some of the advantages of using dual-fuel engines:
- Cost Efficiency: the flexibility of dual fuel engines to allow ship operators to switch fuels depending on availability, cost and environmental regulations makes it worthwhile investment. Also, cost LNG, LPG or Ethanol is less.
- Major advantage of using dual fuel engines is they are environment friendly with up to 0% CO2 emissions, 99% reduction in SOX, 90% reduction in NOX and particulate matters. This makes dual-fuel engines an attractive option for ship operators looking to reduce their environmental impact.
- Long life of engines as the fuel is cleaner, not many deposits, lubrication is easy, and cleaner exhaust as compared to traditional use of fuel so less corrosive action.
Here are some of the disadvantages of using dual-fuel engines:
- Expensive and more complex than traditional ones and needs significant expertise in developing and installing it.
- Dual-fuel engines require additional and specialized equipment such as fuel storage tanks and vaporizers which can add to the cost and complexity of engines.
- Dual-fuel engines have lower efficiency as compared to the traditional diesel engine under low load conditions.
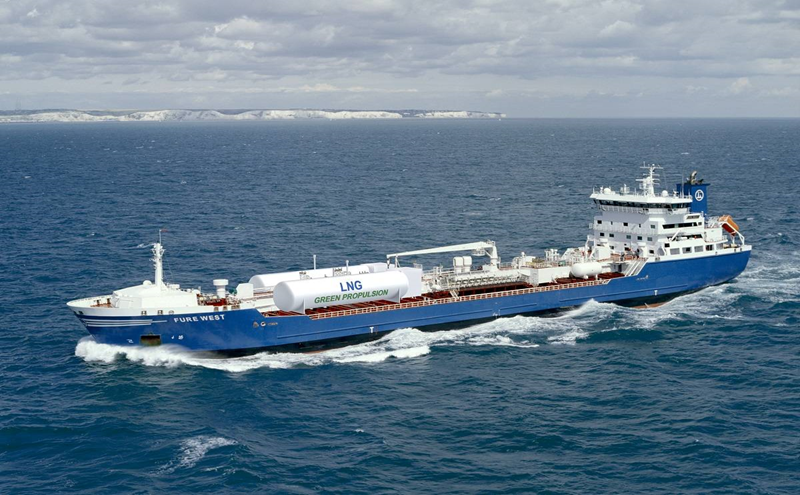
Dual-fuel engines are an excellent choice for LNG carriers, gas carriers and chemical tankers as they provide more flexibility, reduce emissions, and can run on the same fuel they are transporting. As the shipping industry continues to focus on sustainability, DFEs are likely to become even more popular in the years to come.
ATUL KUMAR RAI
JUNIOR ENGINEER