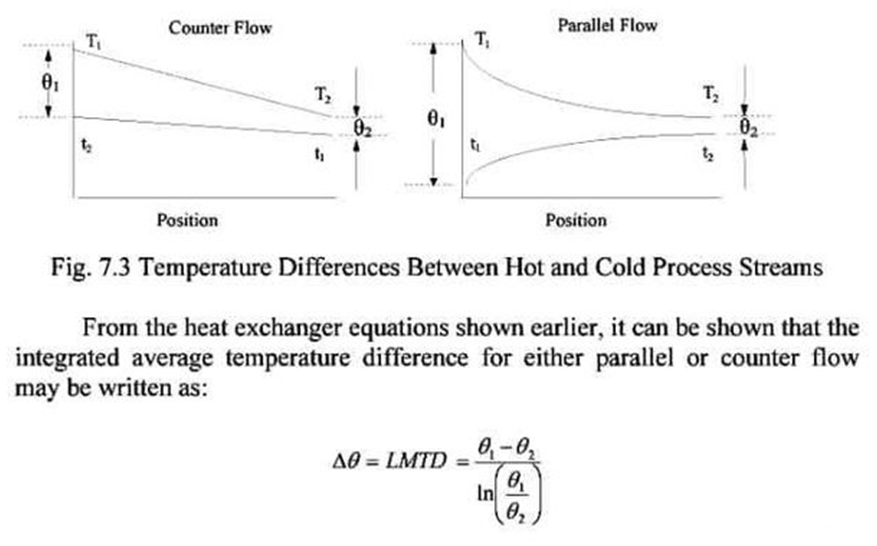
LMTD: it’s a logarithmic average of the temperature difference between the hot and the cold fluid stream at each end of the heat exchanger.
The larger the value of LMTD, higher the heat transfer rate
Rate of heat transfer : Q= U*A*dT
Q= rate of heat transfer
A= heat exchange surface area
dT=LMTD
U= overall co-efficient of Heat Exchanger
- type of fluid
- Flow condition
- Thermal conductivity of wall material
- Thickness of wall
- Cleanliness of wall
Types of flow
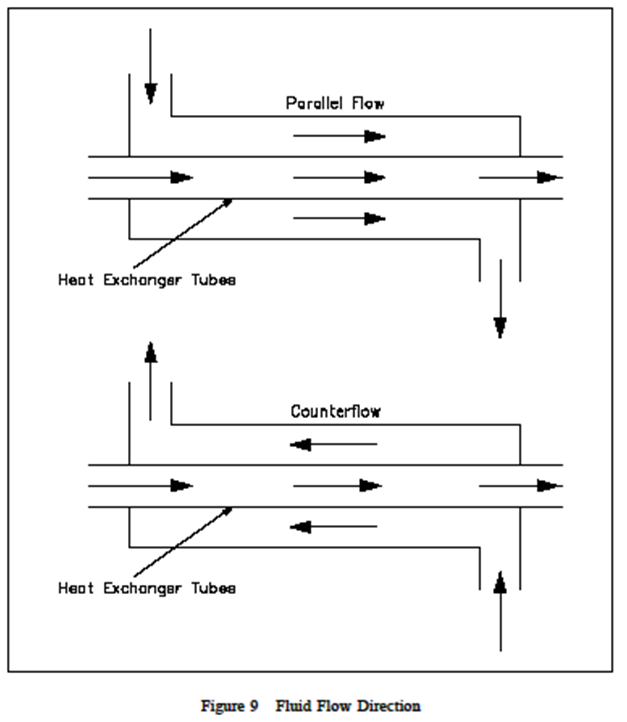
- Parallel flow
- Counter flow
- Cross flow
Draw backs of parallel flow:
- Low rate of HT
- LMTD less
- No use in marine used in food processing units
Cross flow: 90 degree to each other cold and hot fluid
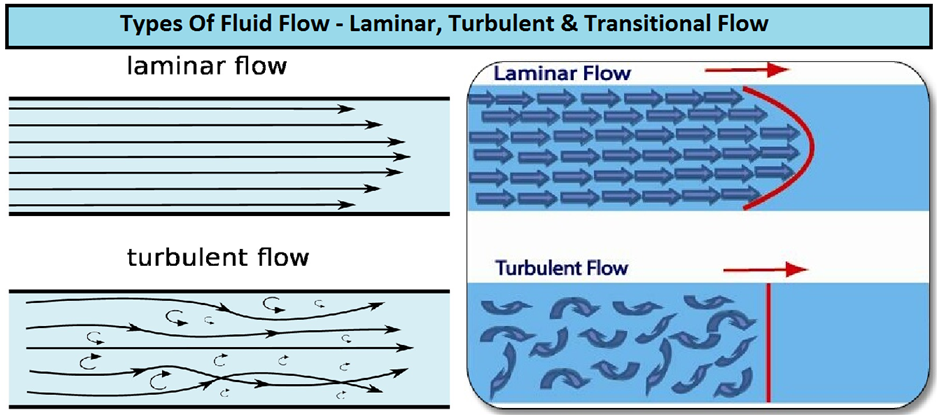
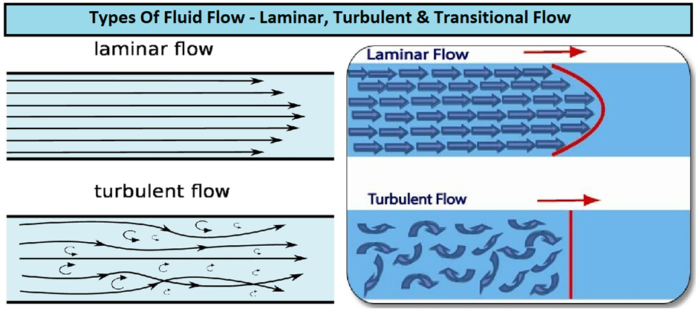
Laminar flow: at walls velocity is less so deposits.
Turbulent flow: good heat transfer rate but erosion.
Types of Heat Exchangers
Shell & tube type:
- most popular
- Cleaning is easy
- Economical
- Frequency of maintenance is high
- More prone to corrosions
- Tube: Al- Brass, Cupro-nickel
- Tube plate: Cast Naval Brass
- Casing & water Boxes: cast iron or Gunmetal
- Baffles: copper or rolled naval brass
- Sacrificial anode: Zinc or Soft iron.
Purpose of Baffles:
- Give rigid structural support to the tubes
- Optimum contact between heat exchanger surfaces
- Prevents coring: with increase or decrease in the temperature of the fluid the velocities also keeps changing.
Causes of tube failure:
- General washing– too much acidic solution
- Impingement attack
- Deposit attack
- Anaerobic attack
- Erosion
- Excess water velocity
Cleaning Fluid: sulphuric acid and citric acid
Leakage test:
- Water test
- Ultra sonic
- Fluorescent
- Vacuum test
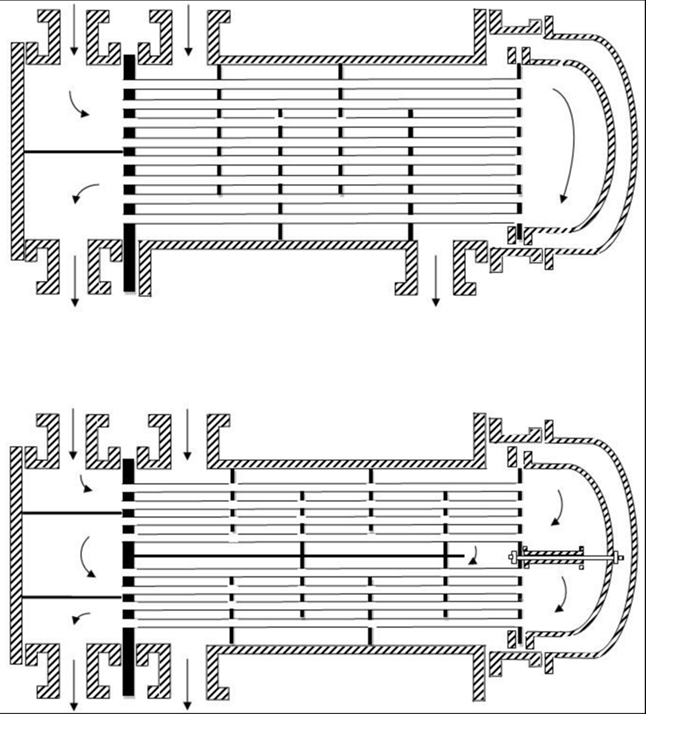
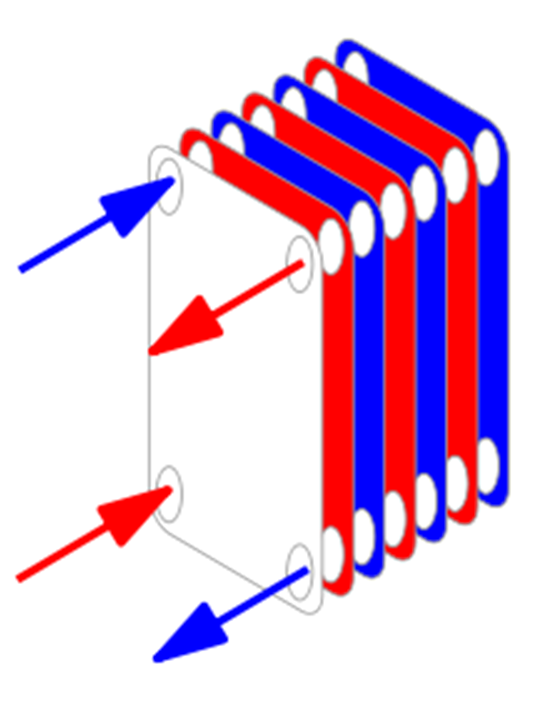
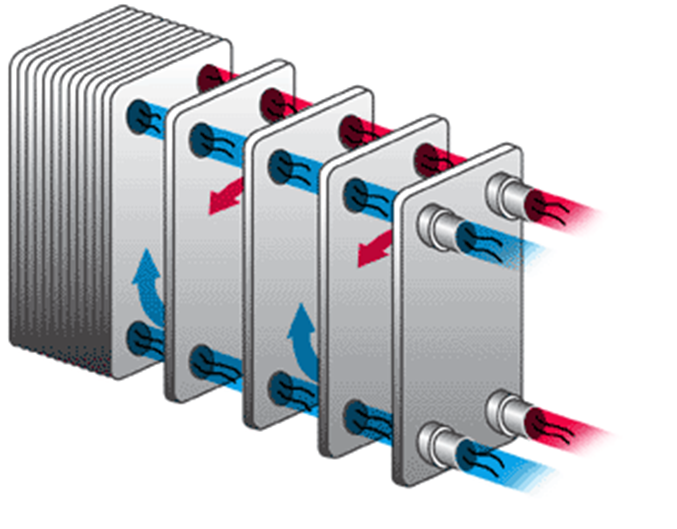
Plate type
- can alter heating or cooling capacity
- Effective in heat transfer
- Costly and cleaning is difficult.
- Plates: titanium , aluminium or titanium brass
- Thickness= 0.5 to 0.8 mm
- Dist= 3 to 5 mm
- Pressure= up to 14 bar
- heating Temp =110 C to 220 C
- Plates are corrugated for high strength and high surface area
- Gasket Nitrile rubber and there are tell tale holes
- C= plate No.
- D= year of manufacture
- E= material identification
- 1st and Last plate doesn’t account for heat exchanging
Advantages:
- No risk of turbulent flow
- Cleaning & inspection is easy
- Wide range of operating temp and pressure
- Compact
Disadvantage:
- Care less cleaning can damage plates
- Costly
SELECTION OF HEAT EXCHANGERS
- Quantity of fluid to be cooled
- Range of temperature(inlet and outlet) to be cooled
- Range of temperature of cooling medium
- Specific heat medium
- Type of medium: corrosive Non- corrosive
- Operating pressure
- Maintenance