A structure which make the base of an engine upon which the bearings and frame are mounted. “The bedplate consists of high, welded longitudinal girders and cross girders with cast steel bearing supports.”

The bed plate is subjected to the following forces:
1. The force of the gas pressure in the cylinder
2. The inertia forces of the moving masses.
3. Side thrust from guide faces
4. Weight of all the engine parts located above bed plate.
5. Torque reaction from propeller
6. Hull deflections
7. Vibration forces due to torque fluctuations, shock loading and thermal stresses
8. Forces due to ship’s movement in heavy seas.
FUNDAMENTAL REQUIREMENT OF BED PLATE
• Strength
• Lightness
• Toughness
• Simple Design
• Access
• Dimensions
• Seal
• Rigidity
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Small engines – single casting of cast iron
Large engines– two longitudinal girders run length of the engine. Connecting these longitudinal girders are the transverse girders positioned between each crank throw. In this there are main bearing pockets for crankshaft. The steel is as per class spec. Usually low carbon steel of carbon content 0.23%
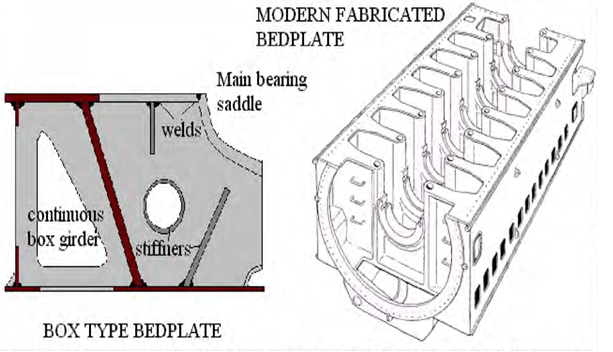
CAUSES FOR BED PLATE TO CRACK
- Cracks can be at the welds where longitudinal joins transverse.
- Under the bearing pockets radial or can be in line.
- Faulty maneuvering Techniques.
- Uneven loading.
- Over loading.
- Slack tie bolts and loose holding down bolts.
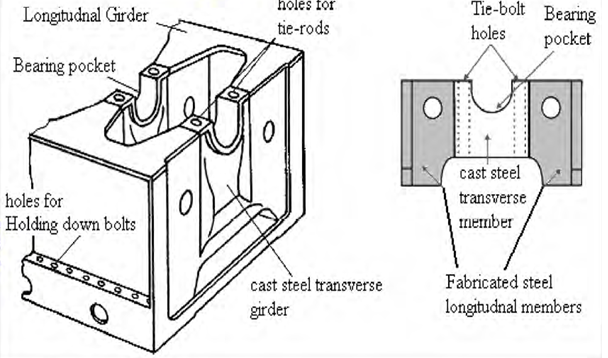
TYPES OF BEDPLATE
The two types of bedplates in general use are as follows:
(i) Trestle type.
(ii) Box form or flat-bottomed type.
TRESTLE TYPE
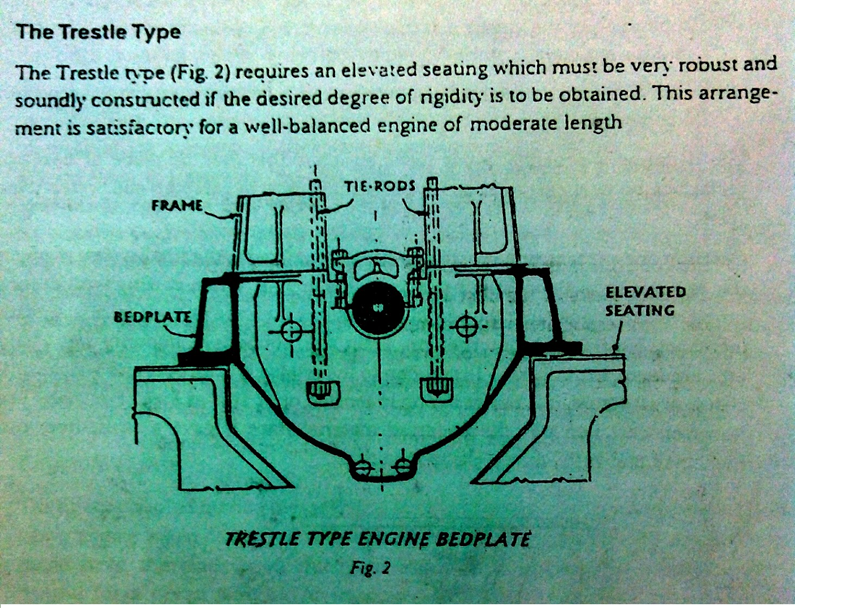
TRESTLE TYPE ADVANTAGES:
- Elevated seating.
- Robust bed plate.
- Rigid transverse.
- Well like structure in double bottom.
- Reduced height.
- Medium sized engines.
BOX TYPE/FLAT TYPE ADVANTAGES:
- Reduced weight.
- Bolted directly to double bottom tank top.
- Can be fabricated.
- Sulzer, MAN B&W uses this.
PRE-FABRICATED ADVANTAGES:
- Good strength against shock loads.
- Modern welding technology Used.
- Easy to repair.
- Vibration characteristics are poor because of various welds.
Complete bed plate is annealed at 600 c… 1hr/25mm of plate thickness.
MATERIAL:
- Cast iron
Hybrid: fabricated mild steel for longitudinal Cast steel for transverse.
MACHINED AREAS
The following surfaces of bedplates are
machined:
(a) Top for frame attachments.
(b) Side for side chocks and entablature cover
plates.
(c) End for thrust block housing, turning gear
and end chocks.
(d) Bottom for chocks, tie bolts, oil sump pan.
TYPES USED
Sulzer RLA
Longitudinals- single plate girder of fabricated steel
Cross girder- part fabricated steel and part cast steel main bearing saddle,
Man-KSZ 70/150 C/CL
Longitudinals-single plate girders of fabricated steel.
Cross girder- fully cast steel welded to longitudinal girder.
Bottom oil pan- flat plate steel, welded.
B& W- GFCA
Longitudinals- single plate girder of fabricated steel
Cross girder -fully cast steel welded to longitudinal girder.
Bottom oil pan- flat plate steel, welded.
FAULTS IN A BED PLATE
- Cracks
- Oil leaks
- Loose chocks