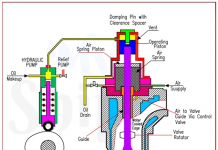
- Pressure Jet Burner: This uses the pressure of the fuel oil to create atomization and a rotating spray. The fuel at the correct viscosity, flow through the centre passage of the burner, so the swirl plate where the pressure energy is converted into tangential velocity energy.
- Rotating Cup Burner: It uses the principle of centrifugal force to increase the velocity of the fuel and thus achieve atomization. The burner unit consists of a heat resistant steel cup, which is fixed to the end of a shaft that is rotated at high speed by an electric motor.
- Y-Type Burner: It atomizes the oil by spraying it into the path of a high velocity jet of steam or air. Either medium can be used, steam is usually more easily available and economical at sea.
- Steam Assisted Burner: In this type of burner, when running at full power, the burner operates as a pressure jet burner and steam and water consumption was kept to minimum.
Feature for efficient combustion of fuel are:
- Flame has to be suspended
- Combustion has to be stable
- Fuel must be finely atomized over required range of output
- Air supplied must be intimately mixed with fuel
- Speed of travel of air and fuel should be same as that of propagation of flame
- Air and fuel must enter the combustion space at the same rate as of combustion gases leaving the furnace
- Time available for the largest drop of fuel must be sufficient for the combustion to complete before the droplet is cooled to a temp less than Its ignition temp.
The ratio of maximum to minimum oil throughput of the burner is called as turn down ratio.