A relay is an electromagnetic switch device which utilizes very small electric current that can turn on or off a much larger electric current. The heart of a relay is an electromagnet.
A relay is an electrically operated switch that responds to change in voltage and current in one circuit, making or breaking contact in other circuit.
e.g. overload relay and overcurrent relay
- Relay measure the operating condition of the equipment. a dash pot is incorporated to provide a time-delay so that to accommodate some rise in current e.g. during starting when rise in temperature is persistent up to the time-delay, the relay trips the circuit without manual intervention and thus prevents the equipment or circuit.
- On the other hand there is a time delay for manual activation even after the alarm and hence equipment may get damaged e.g. push button manually operated.
- Many relays are using electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch. It consist of a coil of wire enclosed around a soft iron core, an iron yoke which provides a low reluctance path for magnetic flux, a movable iron aerate, and one more set of contacts. The armature is pivoted to the yoke and mechanically linked to one or more sets of moving contacts. It is held in place by spring force so that when the relay is de-energized there is an air gap in the magnetic circuit.
- When an electric current is supplied in the coil it generates a strong magnetic field that activates the armature, and the consequent movement of the movable contacts either makes or breaks a connection with a fixed contact.
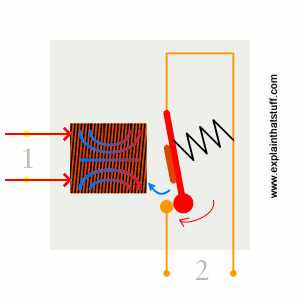

Testing of relay
The set of contacts that are open when the relay not energized are called normally open (NO) contacts and the set of contacts that are closed when the relay is not triggered are called normally closed (NC) contacts.
- Keep the multimeter in the continuity check mode.
- Check for continuity between the NC (Normally closed) contacts and pole.
- Check for discontinuity between NO contacts and the pole.
- Now energize the relay using the rated voltage. For e.g. use a 9v battery for energizing a 9v relay. The relay will engage with clicking sound.
- Now check for continuity between NO(Normally Open) contacts and pole.
- Also check for discontinuity between NC(Normally Closed) contacts and pole.
- For final testing, measure the resistance of the relay coil using a multimeter and check whether it is matching to the value stated by the manufacturer.
All NC(Normally closed) contacts should read 0 ohms to the corresponding pole. All NO(Normally Open) contacts should read in finite resistance to the corresponding pole.
Use independent voltage source appropriate for the rating of the relay coil. If the relay coil is protected by diode, make sure that the independent voltage source is connected with the proper polarity. Listen for a click when the relay is triggered.
In case of energized condition:- use a digital multimeter to test the resistance between each pole of the relay and the corresponding NC and NO contacts for that pole. All NC(Normally Closed) contacts should read infinite resistance to the corresponding pole. All NO(Normally Open) contacts should read 0 ohms to the corresponding pole.
SWITCH

A switch is a mechanically operated circuit interruption device. It’s a “ON” an “OFF” type thing.
A switch is an electrical device that is used for making and breaking the connection in an electric circuit, for the purpose disrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another.
The mechanism of a switch may be operated directly by a human operated to control a circuit (e.g. a light switch), may be operated by a moving object such as a door operated switch, or may be operated by some sensing element for pressure, temperature or flow.
Under high loads or voltages, or dangerous can form when the switch is opened or closed.